

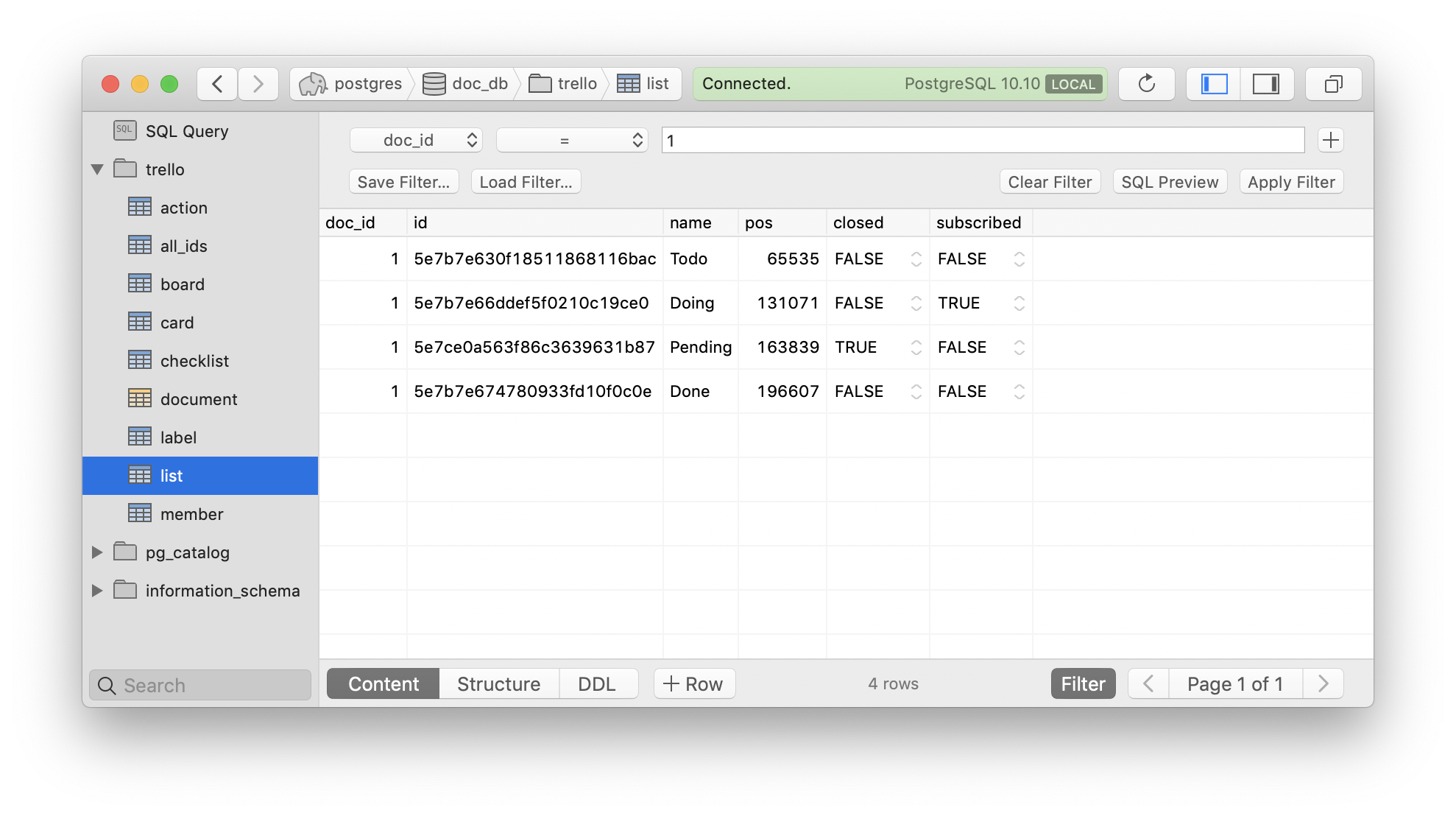
This can result in considerably larger storage footprint compared to MongoDB BSON on WiredTiger or traditional column storage. JSONB storage does not deduplicate the key names in the JSON. JSONB storage results in a larger storage footprint.A more detailed example of this is provided in this blog post – When To Avoid JSONB In A PostgreSQL Schema. This can sometimes result in poor choices like using nested loop joins vs. At this point, PostgreSQL does not store any stats for JSONB columns or keys. Based on this data, the PostgreSQL query planner makes smart decisions on the plan to use for the query. PostgreSQL maintains statistics about the distributions of values in each column of the table – most common values (MCV), NULL entries, histogram of distribution. PostreSQL does not store column statistics for JSONB columns.If PostgreSQL has great support for JSONB, why do we need columns anymore? Why not just create a table with a JSONB blob and get rid of all columns like the schema below: CREATE TABLE test(id int, data JSONB, PRIMARY KEY (id)) Īt the end of the day, columns are still the most efficient technique to work with your data.
#Postgres json query how to
Using JSONB in PostgreSQL: How to Effectively Store & Index JSON Data in PostgreSQL Click To Tweet JSONB Patterns & Antipatterns For the purposes of this blog, when we refer to JSON support in PostgreSQL, we will refer to JSONB going forward. JSONB – however, if you do any further processing, JSONB will be faster.įor example, if you’re just ingesting JSON logs and not querying them in any way, then JSON might be a better option for you.
JSON database in 9.2 was fairly limited (and probably overhyped at that point) – basically a glorified string with some JSON validation thrown in.
If you store each of the keys as columns, it will result in frequent DML operations – this can be difficult when your data set is large – for example, event tracking, analytics, tags, etc. Storing your data in JSON is useful when your schema is fluid and is changing frequently. One of the main reasons to store data using the JSON format is schema flexibility. Why should a relational database even care about unstructured data? It turns out that there are a few scenarios where it is useful.
#Postgres json query download
MongoDB webinar in partnership with PostgresConf to learn more on the topic, and check out our SlideShare page to download the slides. You can also check out our Working with JSON Data in PostgreSQL vs. In this post, we are going to show you tips and techniques on how to effectively store and index JSON data in PostgreSQL. JSON is the most common format used by web services to exchange data, store documents, unstructured data, etc. It is an open standard format which organizes data into key/value pairs and arrays detailed in RFC 7159. JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
